
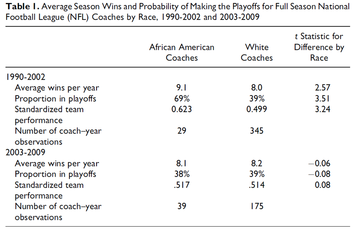
Madden and Ruther (2011) argues that this increase illustrates that there had been discriminatory influences in the previous selection process of new coaches in the NFL. According to Madden & Ruther, discrimination occurs “when the marginal or last African American coach hired must be better than the marginal white coach”. Table 1 below, from Madden & Ruther (2011), details how, prior to introduction of the Rooney Rule, there was a significant discrepancy in the number of African American coaches to white coaches in the NFL. The table also highlights how, prior to the rule, African American coaches enjoyed a significantly higher win rate averaging 9.1 wins a season versus 8.0 of their white counterparts. Sixty-nine percent of African American coaches got their respective teams to the play offs versus thirty-nine percent of all other coaches. Since the Rooney rule however, these discrepancies has evened out and the win rate of African American coaches has decreased.
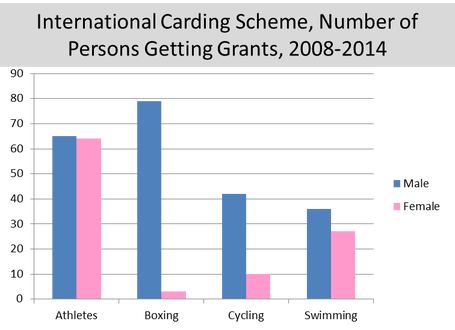
The first chart below highlights that more male athletes have received funding than their female counterparts in all of their respective sports under ICS funding between the discussed years. 65 males were funded in Irish athletics versus 64 female athletes. 79 male boxers were funded versus the mere 3 female recipients. 42 male cyclists were funded as opposed to the 10 female counterparts. And 36 male swimmers were granted funding in comparison to 27 female swimmers.
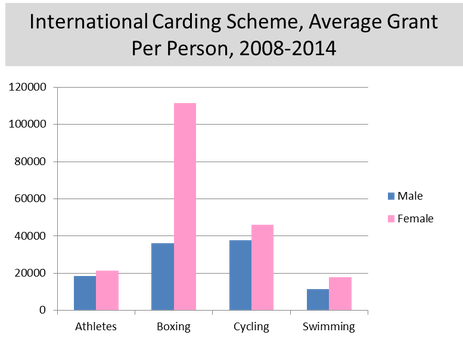
However, these differences still pose some questions. Akin to the African American coaches’ previous higher success rate in the NFL, do Irish female athletes receive more funding versus their male counterparts only because they have to be exceptional in their respective sport to receive funding in the first place? Or, are females athletes funded to a higher level in an attempt to encourage more females into sport? It is hard to say. It requires further investigation.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed